Bunion (Hallux Valgus)
What Is a Bunion?
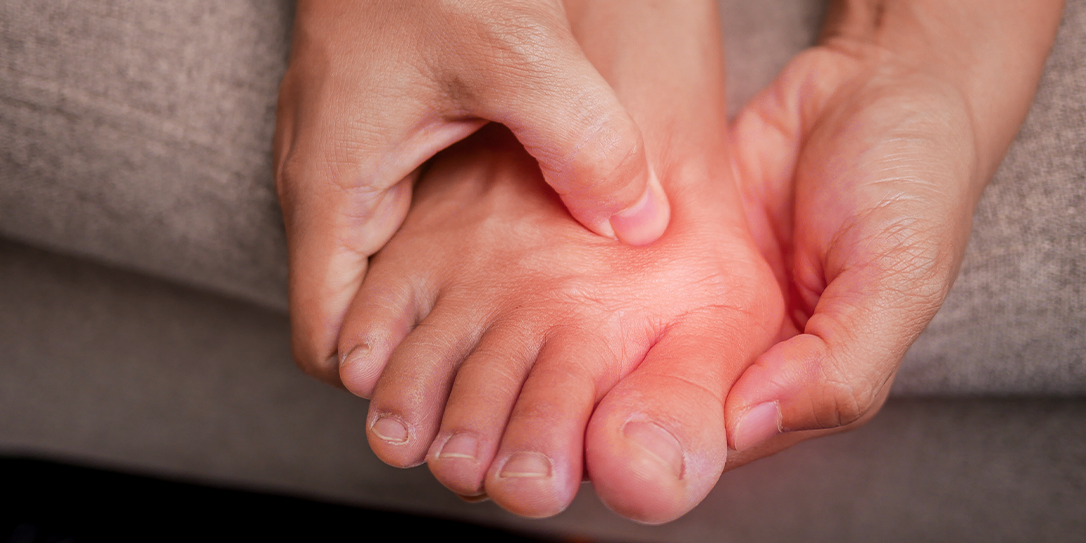
A bunion, also known as hallux valgus, is a type of toe deformity that refers to a bony bump that develops on the inside of the foot at the big toe joint. This usually occurs when some of the bones in the front part of the foot are moved out of place, causing the tip of the big toe to be pulled towards the smaller toe and forcing the joint at the base of the big toe to stick out. There are several types of bunions:
1. Congenital bunions (congenital hallux valgus): This type of bunions are typically present at birth
2. Juvenile or adolescent bunion (hallux valgus): These type of bunions form during childhood and young people aged between 10 to 15 who are diagnosed with flat feet are more likely to develop this type of bunion.
3. Tailor’s bunion: Tailor’s bunion refers to the formation of the bone at the base of the little toe. This formation are usually the result of wearing shoes that do not fit properly or participating in activities that presses the little toe towards the other toes.
Who Are Prone to Getting Bunions?
Soem common risk factors that can incrrease the chances of a buinion development includes:
- Genetics
- Wearing high heals or improper shoes for long peroids of time
- Obesity
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Age
Causes of a Bunion
The causation of bunions comprises of a combination of multiple factors such as genetics, abnormal bone structure and more. However, the most common causes of bunions include:
- Wearing narrow or pointed shoes that crowd the toes
- The way you walk
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Lupus
- Standing over extended peroids of time
Symptoms of a Bunion
- A hard or bony swelling at the big toe joint
- Swelling, redness or soreness arounf the big toe joint
- Corns or calluses where the big toe rubs against the second toe
- Ongoing pain or pain that comes and goes
- Limited range of movement of the big toe
When Should I Seek Help?
Bunions are generally harmless. However, they cannot go away naturally and would require surgery to have it remedied. Furthermore, if you are experiencing the following, it is essential to seek medical help:
- Intense pain
- Interferes with an individual’s ability to wear shoes
- Visible bump on the big toe joint
- Limited range of motion in the foot or big toe
Treatment Options
Non-surgical treatments
Conservative treatments can help manage the condition. These measures include:
- Footwear changes
- Bunion pads or tapping to help cushion the area around the bunion to relieve pressure
- Pain relievers
- Icing
- Physical therapy
- Corticosteroids to help reduce inflammation
Surgical treatments
Surgery may be recommended if conservative methods fail to ease the pain. Furthermore, bunion correction surgery is the only method to remove bunions. This process involves the surgeon making a small incision along the big toe joint to either reposition the big toe, realign the tendons or ligaments around the toe joint, shave off the bunion or remove any parts of the big toe joint.
How Can I Prevent Bunions From Worsening?
- Wear comfortable shoes that are the right size
- Choose shoes that conforms as closely as possible to your foot shape
- Choose shoes with wide insteps, broad toe boxes and plenty of stability
- Observe and record the child’s feet shape as they grow, especially for those that has a family history
- Limit or avoid wearing high heels
- Take breaks in between standing or walking to rest the feet
